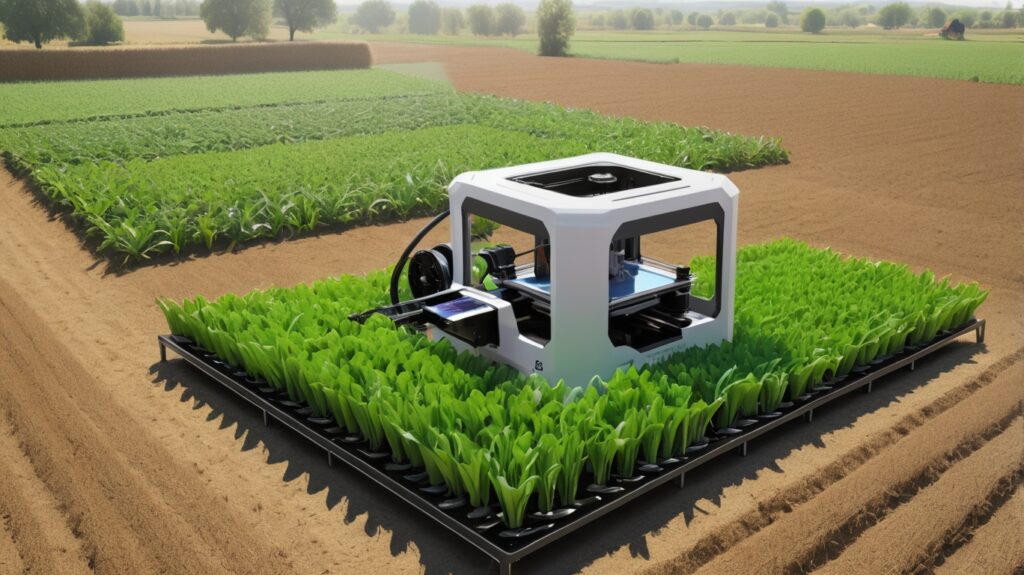
3D Printing in Agriculture: New Possibilities
In recent years, 3D printing has expanded beyond industrial manufacturing and hobbyist projects, finding a quiet yet transformative role in agriculture. This technology, also known as additive manufacturing, offers farmers, researchers, and innovators new ways to solve age-old challenges with precision and creativity. Rather than a sudden revolution, its integration feels more like a natural progression—a tool that complements traditional farming while opening doors to sustainable and efficient practices.
Custom Tools and Repairs
One of the most immediate benefits of 3D printing in agriculture is the ability to create custom tools and replacement parts on demand. Farmers in remote areas no longer need to wait for shipments of specialized equipment; instead, they can design or download models for everything from irrigation components to machinery parts and print them locally. This reduces downtime, cuts costs, and extends the lifespan of existing machinery.
For small-scale farmers, 3D printing allows for the customization of tools tailored to specific crops or terrains. Whether it’s a uniquely shaped planter, an ergonomic hand tool, or a lightweight drone attachment for field monitoring, additive manufacturing enables solutions that are both practical and personal.
Sustainable Innovations
Sustainability is a growing priority in agriculture, and 3D printing supports this shift. By using biodegradable or recycled materials, farmers and agritech developers can produce low-waste tools and prototypes. Some researchers are even experimenting with printing plant-based containers for seedlings, which can be planted directly into the soil, reducing plastic waste in nurseries.
Additionally, 3D printing facilitates the creation of precision agriculture devices, such as soil sensors or micro-irrigation components, which help optimize water and nutrient use. These small but impactful innovations contribute to more resource-efficient farming.
Research and Future Potential
Beyond immediate applications, 3D printing holds promise for future agricultural advancements. Scientists are exploring bioprinting—using living cells to create structures—which could one day lead to lab-grown plant tissues or even customized plant grafts. While still in early stages, such developments hint at a future where farming adapts more dynamically to climate challenges and food demands.
Another area of exploration is 3D-printed hydroponic or aeroponic systems, designed for urban farming and vertical agriculture. These systems can be tailored to fit limited spaces, bringing fresh produce closer to cities while minimizing land use.
A Quiet Transformation
Unlike some high-tech disruptions, 3D printing in agriculture doesn’t seek to replace traditional methods but rather to enhance them. Its strength lies in flexibility—whether helping a farmer fix a broken piece of equipment overnight or enabling researchers to prototype sustainable solutions faster.
As the technology becomes more accessible, its role in farming will likely grow organically, shaped by the needs of those who work the land. For now, it stands as a testament to how innovation, when applied thoughtfully, can cultivate not just crops, but new possibilities.
Would you consider using 3D printing in an agricultural setting? The potential is there, waiting to be explored—one layer at a time.



